What is an NFT?
NFTs (non-fungible-tokens) are encrypted digital records or tokens, that can be used to represent real objects like image, music or video files. These tokens are unique (non-fungible), meaning that they cannot be replaced once created. The tokens are recorded on a network of computers known as a Blockchain.
You can compare an NFT to a file stored on your local computer. You can see when the file was created or modified by looking into your file explorer. Similarly, if your local computer is part of a corporate network, you may also be able to store your file on a central server, where the central server keeps track of when the file was created or modified.
However, unlike traditional networks where the file might be stored on a central server, NFTs are stored on every single computer on the network (Blockchain). So everyone that uses the Blockchain knows the complete history of the file. This is called a decentralised network. This is important because it means that not only can you, the current owner of an NFT know the complete history of the NFT, but everyone else in the world that also uses the Blockchain can also know the history.
What can NFTs be used for?
NFTs can be used for a variety of purposes. Some of the most common uses at present are for creating and storing digital art, music or video. Because the complete history of NFTs can be interrogated by anyone in the world using the Blockchain, NFTs provide a means of determining Provenance or authenticity.
For example, as an artist you may create a piece of art, music or a video and then create an NFT to store a record of that work on the Blockchain. Although copyright laws in most countries would automatically recognise you as the rightful owner of the work, there wasn’t an easy way for potential buyers of your work to establish its provenance or authenticity. Someone could copy your work and try to pass it off as their own, but if you had recorded the work as an NFT and put it on the Blockchain; and only sold the work with the accompanying NFT, your rights in the work would be more secure.
As well as providing a record of the art, the NFT could also be used to provide buyers of your NFT with additional utilities. For instance, as a musician you might create several NFTs of a track you recorded and then allow your fans who purchased say the first 100 copies to acquire a free ticket to your next gig. Each NFT has a unique identification code which facilitates this. Also , what is clear in that example, is that NFTs allow you to build complete communities around your art or cause.
How do NFTs work?
Each NFT is distinguishable from every other NFT on the Blockchain. An NFT has a unique identification code and metadata stored on the Blockchain. The metadata consists of the original digital files (such as an image, music or video file), plus what is known as a “smart contract”: an encrypted contract written in code that sets out the rules of ownership and authenticity of the NFT.
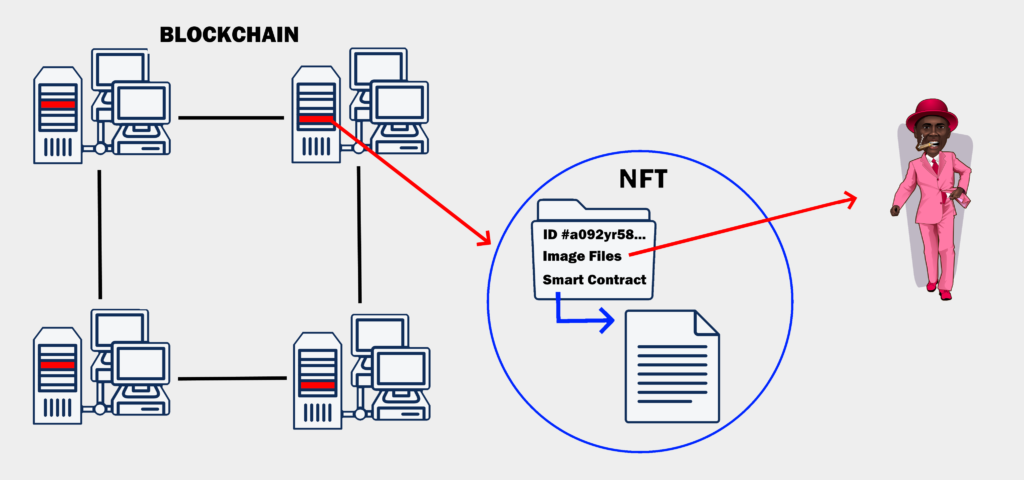
The underlying network of computers called blockchains which support NFTs, are also the same technology on which Cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin, Dogecoin and Ethereum are built. Every node or computer on the Blockchain has its own copy of the history of the NFT: when it was created, bought sold and resold etc.
How are NFTs bought and sold?
NFTs are currently bought and sold on marketplaces using Cryptocurrencies. The biggest marketplaces are Opensea and Rarible. Most of these marketplaces also allow you to create your own NFTs and put them up for sale.
It is important to note that NFTs and cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin are not the same thing. Although both can be purchased with investment in mind, cryptocurrencies have little use beyond there role as a form of digital currency.
The most popular cryptocurrency used to purchase NFTs is Ethereum. Like Bitcoin, Ethereum is a crytocurrency and can be traded like Bitcoin on a cryptocurrency exchange, but the underlying blockchain technology that supports Ethereum, the Ethereum Blockchain, also supports the creation of NFTs.
Other Blockchains are also now providing support for NFTs, and it is this Blockchain technology that provides a myriad of uses for NFTs from holding medical records, real estate (deeds), intellectual property (Patents), academic achievement (Certificates/grades), supply chain (tracking), identity cards etc.
